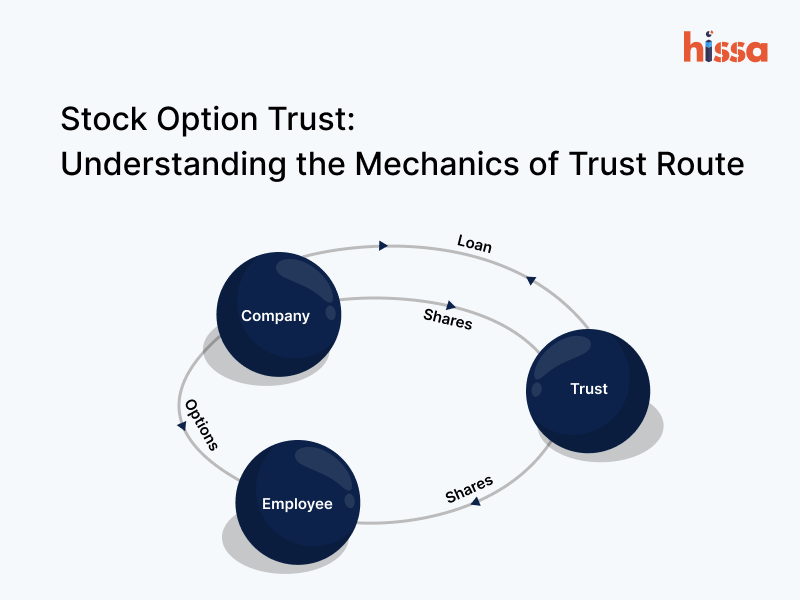
In the competitive world of employee incentives, stock options have emerged as a powerful tool to attract and retain top talent. However, navigating the complexities of stock option plans can be daunting for both companies and employees. Enter the ESOP Trust structure – a modern solution that simplifies the administration and governance of stock options.
An ESOP Trust is a legal framework set up by a company to oversee its stock options. The trust is an extension of the company that holds shares on behalf of employees. By transferring or issuing new shares to the Trust, the company ensures that employees only have beneficial and economic ownership of these shares upon exercising their options
Key Parties in a Trust Structure
1. Trustee
Manages the assets, funds, operations, and finances of the Trust. Trustees must be independent, excluding key management personnel or any person holding more than 10% of the paid-up share capital of the company.
2. Settlor
The company (often the founders) who have created the Trust. The Settlor outlines the Trust’s purpose and initial funding.
3. Beneficiary
Employees who hold stock options and benefit economically from the Trust’s shares.
4. Protector
Typically, a key management personnel appointed to safeguard the interests of the beneficiaries.
Direct Issuance vs. Trust Issuance
1. Direct Issuance
Stock options are granted directly from the ESOP pool, leading to employees appearing on the cap table as shareholders. This can complicate governance and decision-making.
2. Trust Issuance
Employees are beneficial owners, with the Trust holding the legal ownership. This approach simplifies cap table management, controls dilution, and streamlines governance.
Stock Option Trust Structures
Structure 1: Granting Options Following Trust Formation
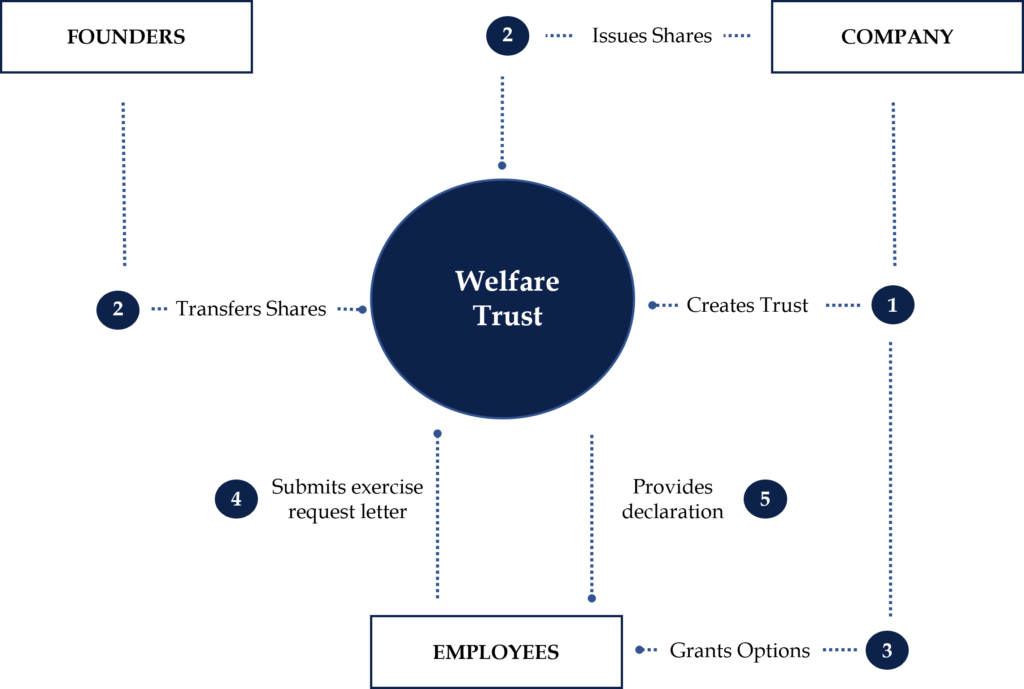
- Company establishes trust for employee stock options and provides loans for share purchase.
- Founders transfer shares to Trust or Company issues shares closer to exercise event.
- Company selects employees for option grants and seeks board approval.
- Employees submit exercise requests to Trust and pay exercise price.
- Trust holds shares for employees, providing necessary declarations.
Structure 2: Creation of Trust After Grant and Exercise of Options
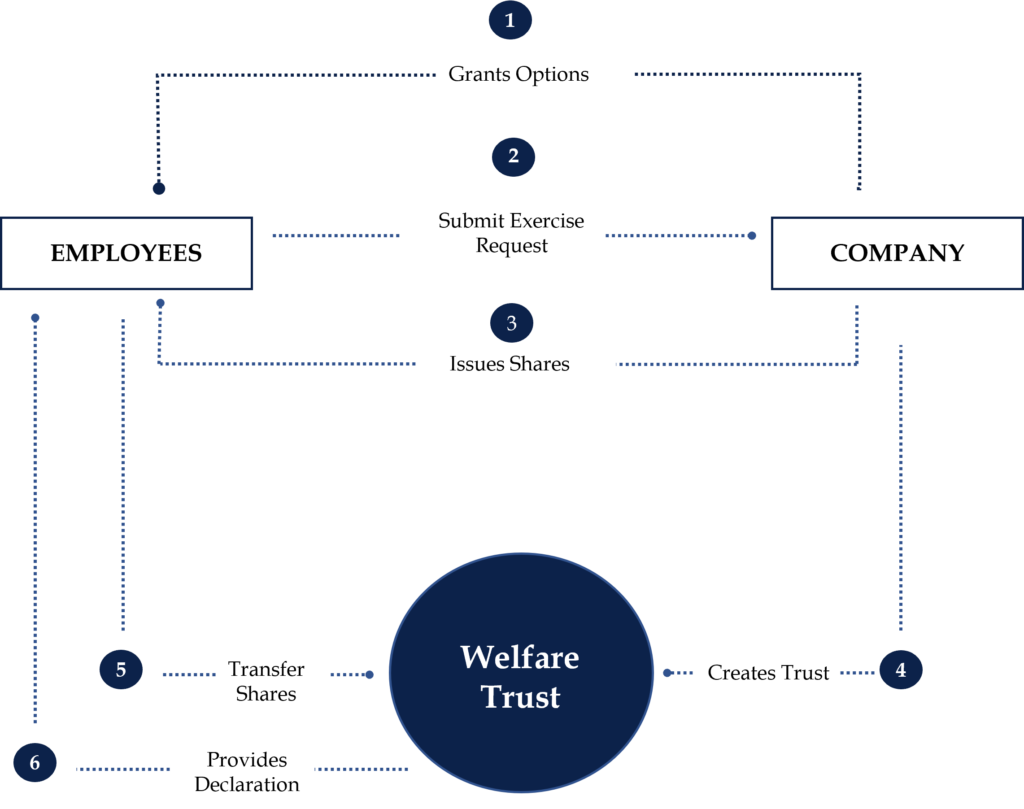
- The company identifies the employees for stock option grants and calls a board meeting to seek approval of the grant.
- Founders transfer shares to Trust or Company issues shares closer to exercise event.
- Employees wishing to exercise their vested options submit the exercise request to the company and pay the exercise/strike price.
- Company issues shares to the employees.
- A company creates a Trust.
- Employees transfer their shares to the Trust. Trust becomes the registered owner of shares and employee the beneficial owner.
Tax Implications
- Company: No tax liability; issues shares on option exercise and deducts tax at source.
- Trust: Capital gain or loss tax applies when the Trust transfers shares to employees.
- Employees: Tax is payable on the difference between fair market value and exercise price at the time of exercise. Capital gains tax applies on the sale of shares.
Challenges of an ESOP Trust Structure
- Funding Requirements: Companies may need to fund the Trust, adding to financial planning complexities.
- Complex Documentation: Additional paperwork and compliance are required, including trustee appointments and PAN/TAN acquisitions.
- Share Management: Unbacked shares due to lapsed or forfeited options can create liquidation issues.
- Administrative Burden: Managing audit and filings related to the Trust adds to the company’s administrative workload.
Benefits of an ESOP Trust Structure
- Professional Management: Trustees handle compliance and administration, reducing the burden on employees.
- Simplified Termination: Easier employee termination processes as employees are not direct shareholders.
- Dispute Mitigation: Legal disputes among heirs do not affect the cap table, avoiding shareholder rights issues.
- Controlled Dilution: Dilution is pre-accounted for, maintaining equity control.
- Governance and Compliance: The Trust ensures robust governance and regulatory compliance.
- Flexibility in M&A: The Trust can transfer shares without requiring grantee consent, simplifying mergers and acquisitions.
- Financing Documentation: The Trust can execute agreements required by investors, ensuring compliance.
The ESOP Trust structure offers significant advantages over direct issuance, including simplified management, controlled dilution, and enhanced governance. As companies seek to align employee incentives with long-term goals, the Trust structure is becoming an increasingly popular choice for effective stock option management.